Science teaches us that whatever goes up must come down. Myths teach us that Titans fall. And history is full of warnings, indicators that can predict future success or failure based on the patterns of previous behavior. Sometimes, all of those lessons can be applied to a situation, particularly one that’s dire enough to be studied, and learned from, and potentially avoided in the future. That’s the case with Lehman Brothers. Before 2008, it was the fourth-largest investment bank in the United States and had been in business for more than 150 years. In September 2008, the company would declare bankruptcy with the largest filing in U.S. history, shaking the world economy and unveiling a tangled web of toxic assets, bad decisions, and litigation. What happened?
To understand how deeply woven Lehman had become in the financial fabric of America, you have to look at its origins. Lehman started as a dry-goods store in 1844. Founded by Bavarian immigrant Henry Lehman, and joined later by his two brothers Emanuel and Mayer, the company soon got involved in commodities trading when it began accepting raw cotton as payment at the store. The brothers started a second business focused only on trading, and it quickly outpaced the store. Henry died of yellow fever in 1855, but the brothers kept the commodities business going. Following the cotton trade as it shifted the center of its orbit to New York City, the brothers opened an office there in 1858.
As that business grew, it took on other markets, like coffee, and expanded into railroad bonds. The company was key in financing the reconstruction of Alabama after the Civil War. In 1889, it underwrote its first public offering. In the 1920s and ’30s, the firm underwrote dozens of further issues, including those for F.W. Woolworth, R.H. Macy & Company, B.F. Goodrich, The Studebaker Corporation, and many more. In a sense, Lehman became big simply by being big and thinking big; it enabled the launch of titans of industry and brands that became household names.
By the financially turbulent 1970s, Lehman had embarked on a series of mergers and acquisitions to stay alive. It acquired Abraham & Company in 1975, then merged with Kuhn, Loeb & Company in 1977. The newly rechristened Lehman Brothers, Kuhn, Loeb Inc. became the fourth-largest investment bank in the U.S. Shearson/American Express bought the company for $360 million in 1984; it in turn merged with E.F. Hutton & Company in 1988. All of this consolidation guaranteed that the renamed Shearson Lehman Hutton would remain a strong institution, but it was also emblematic of the enormous financial power being concentrated into the hands of fewer firms. In 1994, American Express spun out Lehman Brothers Holding, Inc. in an IPO. Chairman and CEO Richard Fuld Jr. would be its final leader.
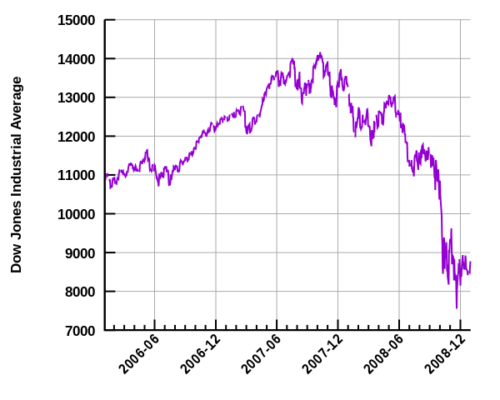
In 1997, Lehman made moves into mortgage origination. It bought BNC Mortgage, a subprime lender, in 2004 to join earlier acquisition Aurora Loan Services. Subprime lending, in theory, allowed people with less substantial credit to secure loans to buy a home. By 2003, Lehman ranked third in such loans. By 2006, BNC and Aurora were lending an astonishing $50 billion a month. By 2008, Lehman’s assets were valued at $680 billion; however, it only had $22.5 billion in firm capital. These were dangerous waters, as market fluctuations could put their entire structure in jeopardy.
Things began to take a negative turn in 2007 as the subprime mortgage crisis began in earnest. Lehman closed BNC, a move that cut 1,200 jobs. At the news of BNC’s closure, Lehman’s stock initially fell only 34 cents. By mid-2008, the company was in much deeper trouble. As reported in The New York Times on August 22, 2008, Lehman’s loss by the second fiscal quarter was $2.8 billion. “What happened was that home delinquencies in the subprime market rose dramatically and spread to the rest of the U.S. housing market,” says Robert Johnson, professor of finance from the Heider College of Business at Creighton University. “The mortgage-backed securities Lehman held in its portfolio fell dramatically in value, and the firm became insolvent and was forced to declare bankruptcy when no willing suitors could be identified.”
Lehman stock dropped 45 percent on September 9 when a proposed takeover by a Korean bank fell through. On September 10, Lehman announced a loss of $3.9 billion; stock dropped 7 percent as it announced further cutbacks in services. One day later, the stock dropped another 42 percent.
In 1997, Lehman made moves in mortgage origination. By 2006, [its subsidiaries] were lending an astonishing $50 billion a month.
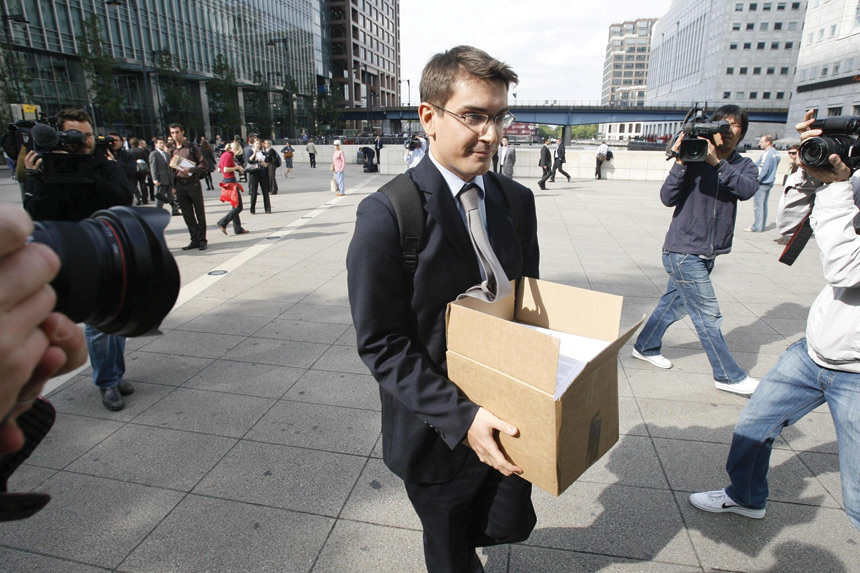
Other forces came into play. Bank of America and Barclay’s emerged as potential buyers, but both passed. By September 15, what had once seemed impossible became inevitable. Lehman Brothers filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy.
The collapse shook the world economy and led to the U.S. government intervening in the form of the Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of 2008, which created the Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP) that allocated $700 billion (capped at $475 billion in 2010 by the Dodd-Frank Act) to buy toxic assets and bolster the financial system.
If we have learned anything, it’s that failures of big banks ripple across the world and cause the greatest damage to ordinary citizens who lose jobs, homes, and security.
How much at risk are we of another recession today, just over 10 years removed from the nadir of the Great Recession? Financial observers are wary. Yes, the Dow hit some highs this fall, but a precipitous drop just before Thanksgiving wiped out the year’s gains. Some experts also point to the fact that today’s long-term bond rates have dipped almost as low as short-term bond rates — a warning sign of an impending economic downturn.
As the saying goes, “History doesn’t repeat itself, but it often rhymes.”
This article is featured in the January/February 2019 issue of The Saturday Evening Post. Subscribe to the magazine for more art, inspiring stories, fiction, humor, and features from our archives.
Become a Saturday Evening Post member and enjoy unlimited access. Subscribe now




Comments
How do I find info on DAMSON stock that my dad bought thru SHEARSON/AMERICAN EXPRESS IN 1983-85